Facial Pain
The Facial Pain Management section at the Pain Center offers comprehensive medical services to ease facial pain that can cause mild to severe discomfort in patients. As in head and neck pain cases, the first step in correctly diagnosing the problem is to give the patient a number of questionnaires to fill out. A Pain Center dentist will then give the patient a thorough examination. Following that, a battery of medical tests may be performed, including image scans, lab tests and psychological evaluations, as well as nerve blocks and other techniques that can uncover important clues to the causes of the condition. Once all the data is gathered, a team of doctors from various medical specialties consults together to analyze the information and develop a customized treatment plan to relieve or manage the individual's pain. Because of the complex nature of pain, treatment plans are organized in a very precise way and conducted over a limited period of time, usually six to eight weeks. Patients are not required to stay in the hospital for any of the treatments. The center's doctors consider the patient a key team member. In eliminating, reducing and managing ongoing pain, success depends highly on the patient's willingness to cooperate fully and follow closely every step in the treatment process.

Causes
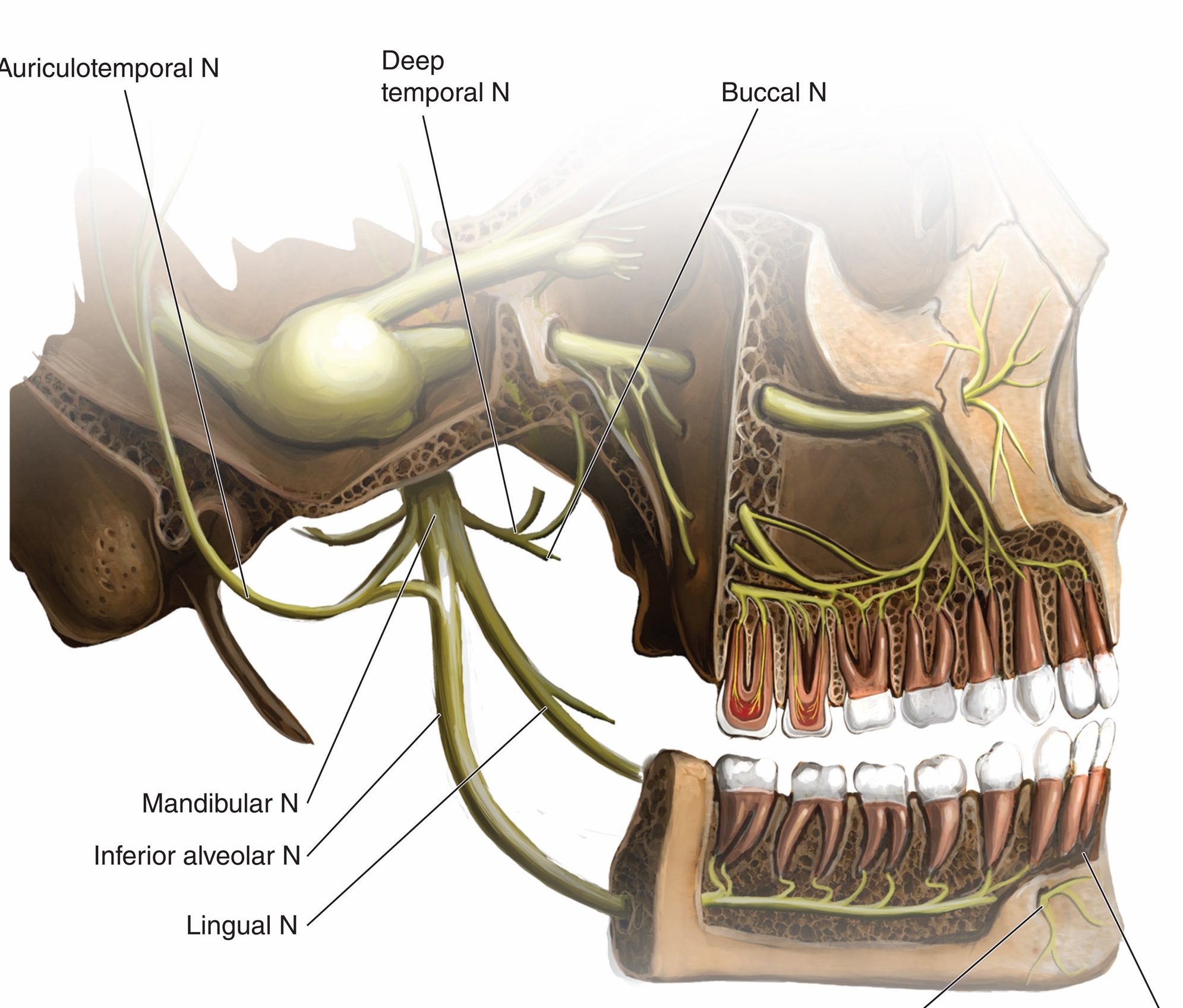
- Trigeminal neuralgia (pain in the lips, gums, cheek or chin)
- Trigeminal dysesthesia (abnormal feeling in the lips, gums, cheek or chin)
- Post-surgical and post-traumatic face pain
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (tongue pain or pain in the pharynx)
- Post-herpetic neuralgia
- Facial Musculoskeletal Pain
- Temporomandibular disorders (also known as TMJ, or pain in the joint that connects the jaw to the skull)
- Myofascial pain (face muscle disorders causing spasms, limited motion and other symptoms)
- Facial Spasms
- Hemifacial spasm (sudden muscle contraction on one side of the face)
- Torticollis (muscle contraction that causes the neck to twist unnaturally)
- Myoclonus (muscle twitching)
- Blepharospasm (twitching of the eyelid)
- Facial Paralysis
- Bell palsy (paralysis of one side of the face)
- Post-surgical paralysis
- Post-stroke paralysis
Treatment
- Pharmacotherapy (medications)
- Physical therapy
- Splint therapy
- Behavioral therapy
- Nerve blocks
- Botulinum injections
- Surgery
Types of Pain
- Neck Pain
- Low Back Pain
- Thoracic Spine Pain
- Headache
- Shoulder Pain
- Elbow Pain
- Wrist Pain
- Knee Pain
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Neuropathic Pain Syndromes
- Fibromyalgia And Other Myofacial Pain Syndromes
- Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome
- Facial Pain
- Foot Pain
- Abdominal Wall Pain Syndrome
- Sacroiliac Joint Pain
- Cancer Pain
- Urogenital Pain Syndrome
- Chronic Pelvic Pain